16.08.2012
Australian researches found receptors in charge of addiction to opiates.
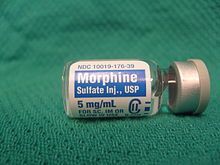
Morphine used in medicine as an analgesic blocks the signals of pain going to the brain, causing a sense of euphoria and comfort instead. However, its use as a medicine is significantly complicated by a serious addiction it causes.
A group of researchers led by Mark Hatchinson representing the University of Adelaide made an experiment. A group of mice received only morphine, while the other group received its mixture with a drug which blocks TLR-4 immune system receptors. The mice of the second group have demonstrated no signs of the addiction, though their susceptibility to pain decreased as well as the first group’s. Besides, the brain of the mice produced much less dopamine causing the sense of euphoria.
To check up the results of the experiment, the researchers also managed to develop a breed of mice having no TLR-4 receptors. The effect was the same as in the case when the mice received the blocking drug.
The discovery will allow to use morphine for medical purposes without causing addiction. Further, it will promote creating new ways of treatment of drug addiction.